- Published on
- • Views
Internship Report: Reflections on Professional Learning
- Authors
- Name
- Anirudh Mitra
- @BrownVitriol
Table of Contents
- Abstract
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- 1.1 Testbook
- 1.2 Overview of the Role
- 1.3 Responsibilities
- Chapter 2: Technology Stack
- 2.1 Overview
- 2.2 Communication & Task Management
- Chapter 3: Prerequisites
- 3.1 First Step
- 3.2 Second Step
- Chapter 4: Onboarding Tasks & Ad-Hocs
- 4.1 Onboarding Tasks
- 4.2 Ad-Hocs
- Chapter 5: Product Tasks
- 5.1 IAS Preparation Blog Migration
- 5.2 Custom Pages SEO Optimization
- 5.2.1 About SEO
- 5.2.2 Field Work
- 5.3 Addition of 'Also Read In' Badge
- 5.4 Exam Calendar Content & SEO Update
- 5.5 Adding Support for Multiple Languages in Custom Pages
- 5.5.1 Design & Planning
- 5.5.2 Challenges
- 5.5.3 Results
- 5.6 Current Affairs Blog Migration
- 5.7 Multi-level Breadcrumbs
- 5.8 Making Popups Scalable Across Web and Mobile Platforms
- 5.9 Location Based Popups
- Chapter 6: Engineering Tasks
- 6.1 Performance & Page Speed Improvement
- 6.1.1 Background Research
- 6.1.2 Field Work
- 6.2 Static Rendered Pages
- 6.2.1 Design & Planning
- 6.2.2 Approach
- 6.3 Improved Deployment Process with Jenkins API Selection
- 6.4 Extras
- 6.4.1 Internal Library Improvement and Development
- 6.4.2 Universal Analytics to Google Analytics Migration
- Bibliography
Abstract
This report summarises the work done by me on the frontend stack, which includes Angular, AngularJS, SCSS, Docker, Jenkins, TypeScript, JavaScript, and other internal tools, during my internship as an SDE Intern at Testbook.com. Testbook.com is a private corporation that specializes in developing preparatory content for competitive exams including lectures, quizzes, exams, and so on. The responsibilities of a Software Development Engineering (SDE) intern are to work on Project Development from different departments and provide Technical Support and solve the queries of the customers. The chapters in this report, in brief, cover the technologies used, the tools developed, the challenges faced, and the solutions implemented during the development phase. Overall, the development process aided in the process of creating a robust and efficient system that forms the foundation of Testbook's ed-tech platform.
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Testbook
Testbook.com is an online learning platform that offers courses, study materials, and practice tests for various competitive exams in India. The platform provides a wide range of courses, including banking, railways, SSC, insurance, and engineering entrance exams, among others. It also offers mock tests and previous year question papers for students to practice and improve their skills. Testbook.com aims to provide accessible and affordable education to everyone and has a team of experienced educators and subject matter experts to create high-quality content for its courses. The platform has helped thousands of students across India to prepare for and succeed in various competitive exams.
1.2 Overview of the Role
As an intern, a software developer may be responsible for various tasks such as writing and testing code, fixing bugs, designing software features, and participating in team meetings. The internship aims to give the intern hands-on experience working with real-world software development tools and methodologies.
1.3 Responsibilities
- Build user-friendly websites and applications that meet customer needs
- Ensure the responsiveness and quality of applications
- Collaborate with back-end developers and web designers to improve the usability
- Integrate data fetching APIs with the user interface ensuring a minimal footprint and the best possible performance.
Chapter 2: Technology Stack
2.1 Overview
A tech stack, or technology stack, is a collection of software technologies and tools that are used together to build and run a web application, mobile app, or any other software system. A typical tech stack includes multiple layers or components, each responsible for different aspects of the application.
Here's an overview of a technology stack the team at Testbook utilizes:
- Front-end: AngularJS and Angular are both popular front-end frameworks used to build dynamic and responsive web applications. AngularJS is an older version of Angular, but it's still widely used in legacy applications. Angular, on the other hand, is a more modern and powerful framework that offers better performance and features.
- State management: NGRX is a state management library for Angular that provides a reactive and scalable approach to managing application states. It's built on top of RxJS and provides a predictable and consistent way to manage complex application data.
- Containerisation: Docker is a containerisation platform that allows developers to package their applications and dependencies into a portable container that can be deployed on any platform. It provides a lightweight and secure way to deploy and run applications in different environments.
- Continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD): Jenkins is a popular open-source CI/CD tool that automates the process of building, testing, and deploying software. It provides a pipeline-based approach to building and deploying applications and supports a wide range of plugins and integrations.
- Back-end: Golang is a programming language that is widely used for building high-performance back-end systems. It offers a simple syntax, excellent concurrency support, and efficient memory management, making it a popular choice for building scalable and reliable applications.
- Database: MongoDB is a popular NoSQL database that provides a flexible and scalable approach to storing and retrieving data. It supports a variety of data structures and provides a document-based model that makes it easy to store complex data.
- Cloud platform: Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a cloud computing platform that provides a wide range of services and tools for building, deploying, and scaling applications. It offers a scalable and reliable infrastructure for hosting applications, along with services like storage, networking, and machine learning.
This tech stack combines modern front-end and back-end technologies with containerisation, CI/CD, and cloud infrastructure to provide a scalable and reliable platform for building and deploying applications. The specific technologies and tools used in a tech stack can vary depending on the requirements of the application, the preferences of the development team, and the available resources. Choosing the right tech stack is an important decision for any software development project, as it can impact the performance, scalability, and maintainability of the application.
2.2 Communication & Task Management
At a tech company, effective communication and task management are critical for ensuring that teams can collaborate and work efficiently towards their goals. Here's an overview of some common tools and strategies used for communication and task management in a tech company:
- Communication tools: There are various communication tools used by tech companies to facilitate collaboration and communication among teams.
- Instant messaging: Instant messaging tools allow teams to communicate in real time, share files, and organize conversations by channels or topics.
- Video conferencing: Video conferencing tools enable remote teams to hold virtual meetings, share screens, and collaborate in real time.
- Project management tools: There are various project management tools that tech companies use to manage their tasks and projects, including:
- Agile methodologies: Agile methodologies like Scrum or Kanban are widely used in tech companies to manage their projects and tasks. These methodologies are based on iterative and incremental development, where teams work in short cycles or sprints to deliver working software.
- Daily stand-up meetings: Daily stand-up meetings are a common practice in tech companies, where team members gather for a brief meeting to share updates, discuss blockers, and plan for the day ahead.
Effective communication and task management are critical for the success of any tech company. By using the right tools and methodologies, teams can collaborate efficiently, stay on track with their goals, and deliver high-quality products and services.
Chapter 3: Prerequisites
3.1 First Step
The Prerequisites for working with the above-mentioned stack were as follows:
- Angular: Knowledge of TypeScript, HTML, and CSS; understanding of Angular concepts such as components, services, and directives; familiarity with Angular CLI and related tools.
- NgRx: Knowledge of Redux concepts and principles; understanding of Angular concepts such as components, services, and observables; experience using NgRx to manage state in an Angular app.

- Docker: Understanding of containerization concepts and principles; experience using Docker to build, deploy, and manage containers; knowledge of Dockerfile syntax and Docker Compose.
- Jenkins: Understanding of continuous integration and continuous delivery concepts and principles; experience using Jenkins to automate build, test, and deployment processes; knowledge of Jenkinsfile syntax.
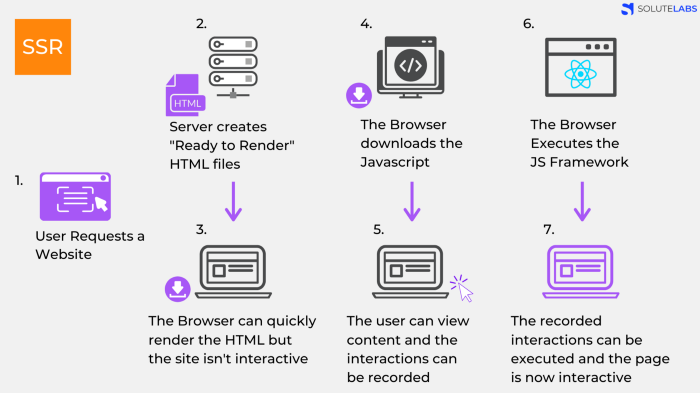
- Angular Universal: Familiarity with server-side rendering concepts and principles; knowledge of Node.js and Express; experience setting up and configuring an Angular Universal app.
3.2 Second Step
To work effectively in a tech team, having strong soft skills, such as communication, teamwork, problem-solving, and time management is also important. Additionally, having a growth mindset and a willingness to learn and adapt to new technologies and methodologies can help succeed as a software developer.
Chapter 4: Onboarding Tasks & Ad-Hocs
During my internship, I worked on several projects which are listed below in chronological order:
4.1 Onboarding Tasks
The internship began with onboarding tasks designed to help the user learn and understand the Angular framework and the development environment setup.
- The first task was to complete the Angular Tour of Heroes tutorial, which provided an introduction to Angular core concepts such as components, services, and observables.
- The user also worked on setting up the development environment, including installing the necessary tools such as Docker, NVM(Node Version Manager), Node.js, Angular CLI, and Visual Studio Code.
- These small tasks helped the user get familiar with the development environment and the Angular framework, which was essential for the rest of the projects worked on during the internship.
4.2 Ad-Hocs
In project management, ad-hoc refers to something that is done or created for a specific or immediate purpose, without prior planning or preparation. Ad-hoc tasks or solutions are often created in response to a specific problem or situation that arises, rather than as part of a larger, pre-existing plan or strategy. During my internship at Testbook, I was assigned many ad-hoc tasks that solved immediate breaking changes or patched bugs that existed for a long time. Some of them were:
- Code Cleanup: Removing components that are not currently in use and conducting a cleanup to streamline the codebase and improve its efficiency.
- Fixing Typos: Correcting typing errors and updating older values on a content-heavy website helps to ensure a polished and professional presentation of information to the audience.
- Fixing Broken Links: Fixing broken links on a website enhances the user experience by ensuring that visitors can easily navigate and access all relevant content without encountering frustrating dead ends.
- Resolving Redirection Issues: Resolving redirection issues on a website helps to ensure a seamless user experience by preventing visitors from encountering broken or irrelevant links and directing them to the intended content efficiently.
- Adding New Hyperlinks: Adding hyperlinks to a website can significantly enhance its search engine optimization (SEO) by improving the site's visibility and authority. Additionally, linking to relevant and credible sources can also enrich the user experience by providing additional context and resources on a given topic.
- Debugging & Rectifying Incorrect Data issues: Remediating data issues is crucial for maintaining data integrity and ensuring the accuracy of information presented to users. My part was to find the source of the wrong data and then help the corresponding team(content/marketing/backend) fix it.
- Adding Meta Tags to Different Pages: Adding meta tags is important because it improves search engine visibility, enhances the user experience, and optimizes social media sharing. My tasks were focused on updating the meta information and adding new tags following the policies shared by Google, Bing and other such search engines.
- Fix Spacing Issues Across Site: Inconsistent or excessive spacing can hamper the user experience. I debugged the code and found reasons for the same, and then rectified them.
- Updating Robots.txt File: I have completed the task of updating the robots.txt file to control search engine crawler access to the website. By specifying which pages should and should not be crawled, I improved the website's indexing and search engine visibility. Furthermore, this update ensures that sensitive or irrelevant pages are excluded from search results, which enhances the user experience and protects user privacy.
- Setting Limits for API Response: It is an important optimization technique for controlling the amount of data returned by an API. By limiting the amount of data, websites can reduce the load on their servers, improve performance, and prevent unnecessary bandwidth consumption.
Chapter 5: Product Tasks
After completing the onboarding tasks and fixing some bugs and issues, I was assigned
tasks from the product side.
5.1 IAS Preparation Blog Migration
My first major task was to migrate the existing IAS Preparation pages from the blog to new custom pages and ensure smooth functioning without any downtime on these pages.
- Migrated IAS Preparation pages from the old WordPress blog setup to the new Angular codebase under the custom pages,
- Integrated with existing features and product pitches,
- Understood existing codebase,
- Created new components, services, and injectables,
- Tested the new code thoroughly to ensure a smooth transition for the users,
- The project was successfully completed and integrated into the existing platform.
5.2 Custom Pages SEO Optimization
5.2.1 About SEO
SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is the process of optimizing a website's technical and non-technical elements to improve its visibility and ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs). This involves implementing strategies to increase the website's relevance, authority, and trustworthiness in the eyes of search engines, such as improving website architecture, content quality and relevance, user experience, and building high-quality backlinks. The goal of SEO is to attract more organic traffic to a website, improve user engagement and conversion rates, and ultimately drive business growth and success.

5.2.2 Field Work
My contributions majorly fall into:
- Fixing header tags(H1, H2, P, etc) position and font-size,
- Adding canonical links,
- Adding Hreflang meta tags and fixing wrong tags,
- Organization Schema fixes,
- Article Schema fixes,
- Adding FAQ & FAQ Schema.
5.3 Addition of 'Also Read In' Badge
The task was to add ”Also Read In” badges in the header of the web pages to make pages in other languages more accessible. This badge will allow users to easily switch between different language versions of the page, ensuring that our content is accessible to a wider audience alongside content being more exposed to search engines as the badge contained anchor tags. It was an important step in linking Marathi and Bengali pages because they were fairly new and required more exposure and backlinking.
5.4 Exam Calendar Content & SEO Update
The task was to update the content and meta tags of the exam calendar page. This was important to ensure that the page is informative, up-to-date, and optimized. The calendar was previously programmed to show recent exams and the content was automated through Google Sheets. It was critical that the page continues to function properly and displays the most current and accurate information.
5.5 Adding Support for Multiple Languages in Custom Pages
This was an important part of the big project to make the whole website multi-lang and more accessible to the public by providing content in vernacular languages.
5.5.1 Design & Planning
The task can be divided into the following parts:
- Review the existing custom pages on the website and identify areas that need to be updated for multi-language support.
- Implement the selected language featured into the custom pages, ensuring that the language switcher is functional and user-friendly.
- Test the functionality of the multi-language support feature, including the language switcher, page content, and URL routing.
- Make necessary adjustments based on user feedback and any issues that arise during testing.
5.5.2 Challenges
One of the challenges we faced was ensuring that the multi-language support feature was fully integrated with the existing support for site language switching to enable easy management and updating of multi-language content while driving everything from a single point of operation. Additionally, we had to consider how to maintain search engine optimization (SEO) while implementing the language switcher and handling translated URLs.
5.5.3 Results
After implementing multi-language support for custom pages, users can now access our content in multiple languages, including Spanish, French, and Chinese. The language switcher allows users to easily switch between languages, and translated URLs are properly handled to maintain SEO. The feature has received positive feedback from users and has helped to improve user engagement and satisfaction.
5.6 Current Affairs Blog Migration
This task was similar to IAS Preparation Migration. The current affairs and general knowledge pages were earlier served through the blog platform and the task was to move them to new custom pages.
5.7 Multi-level Breadcrumbs
For the task of adding support for multi-level breadcrumbs, the work involved implementing a new set of keys into the angular app, testing and adjusting the feature, and ensuring proper integration with the content management system and website structure. The application of this feature allows users to easily navigate through multiple levels of pages and categories, improving website navigation and user experience. This feature has become a common navigation element in modern websites and is useful for sites with deep navigation structures or complex hierarchies of content. It also enabled the content team to create a level of logical grouping between the pages.
5.8 Making Popups Scalable Across Web and Mobile Platforms
For this task, the work involved designing and implementing a system that pulls popup content and settings from a single Google Sheet and dynamically generates the popups on the website. The application of this feature is to make it easier for content managers and marketers to create and update popups without needing technical expertise or requiring assistance from the developers every time a sale needs to go live. This was a fairly large project and took about 3 weeks to design, develop, test and deploy. This project also required me to work on different internal libraries and change the existing flow.
5.9 Location Based Popups
This task was done as a follow-up to Pop-up Scalability. The aim was to run location-based campaigns in 5 different states and show the user pop-ups relevant to their location. To achieve this, we added a location detection feature to the popup system that used the user’s IP address to determine their location. The system then checked the relevant state in the Google Sheet and displayed the corresponding popup for that location. The application of this feature allowed the business to deliver targeted messages or promotions to users in specific geographic locations, resulting in a more personalized and engaging user experience.
Chapter 6: Engineering Tasks
6.1 Performance & Page Speed Improvement
As part of engineering tasks, I studied various metrics that contribute to calculating a web page’s performance and page speed. I then made efforts to improve those metrics for exam pages which are mostly static and content-heavy.
6.1.1 Background Research
Some of the metrics that I studied to improve the performance and page speed of the exam pages include:
- First Contentful Paint (FCP): FCP measures the time taken for the first piece of content to be displayed on the screen
- Time to Interactive (TTI): while TTI measures the time taken for the page to become fully interactive
- Total Blocking Time (TBT): TBT measures the time taken for the page to respond to user inputs.
6.1.2 Field Work
To improve these metrics, I first optimized the code by removing unnecessary code and reducing the number of HTTP requests. I also implemented lazy loading to reduce the initial load time of the page. Additionally, I used caching to store frequently accessed data on the client side to reduce the number of server requests. I also employed minification and compression techniques to reduce the size of the code files and files being sent from the server to the client. Image optimization was also implemented to reduce the size of images and ensure they are displayed correctly on different devices.
Finally, I monitored the performance of the exam pages regularly using tools such as Lighthouse score/Google PageSpeed Insights and identified areas for improvement. I was able to provide a faster and more responsive user experience, especially for users accessing the pages on slower internet connections or devices with limited processing power.
| Metric | Before | After |
|---|---|---|
| FCP | 0.5 s | 0.4 s |
| TTI | 2.2 s | - |
| SI | 1.3 s | 0.6 s |
| TBT | 440 ms | 0 ms |
| LCP | 0.6 s | 0.6 s |
| CLS | 0 | 0.001 |
6.2 Static Rendered Pages
The aim of the project was to improve website performance, reduce server load, and optimize search engine optimization (SEO) by serving static HTML and CSS files that can be very efficiently cached.
6.2.1 Design & Planning
My role was to identify the technical requirements and implement the necessary changes to the existing Angular server-side rendered pages, with a focus on static rendering.
6.2.2 Approach
- The first step was to switch from the Angular Universal server-side rendering approach to static rendering using a custom Express server setup.
- Next, used internal tools and libraries to make the static pages interactive and performant. This included using JavaScript to enhance the user interface and enable client-side interactivity, as well as optimizing the performance of the page using techniques such as lazy loading and caching.
The approach resulted in faster load times, improved reliability, and better search engine
rankings, leading to a better user experience and increased customer satisfaction.
6.3 Improved Deployment Process with Jenkins API Selection
The objective of this project was to enhance the deployment process of a web application by utilizing an API selection option in Jenkins and implementing a CI/CD pipeline. As a developer, my responsibilities included:
- Updating the application code to add the dropdown for selecting which API the application should point to,
- Configuring Jenkins,
- And updating the existing pipeline to incorporate the changes.
The implementation of an API selection option in Jenkins and the CI/CD pipeline improved the deployment process significantly. The deployment process became faster, more efficient, and more reliable. With the automated deployment process and CI/CD pipeline, every developer in the team was saved from repeated tasks of changing the API environment every time they wanted to test their code. This also saved time in Pull Request reviews.
6.4 Extras
6.4.1 Internal Library Improvement and Development
6.4.2 Universal Analytics to Google Analytics Migration
Bibliography
[1] Testbook.com, ”About Us,” Testbook.com, [Online]. Available: https://testbook.com/about-us. [Accessed April 1, 2023].
[2] Angular, ”Angular,” Angular.io, [Online]. Available: https://angular.io/. [Accessed April 1, 2023].
[3] NGRX, ”NGRX Documentation,” NGRX, [Online]. Available: https://ngrx.io/docs. [Accessed April 1, 2023].
[4] Docker, ”Docker Documentation,” Docker, [Online]. Available: https://docs.docker.com/. [Accessed April 1, 2023].